November 2013
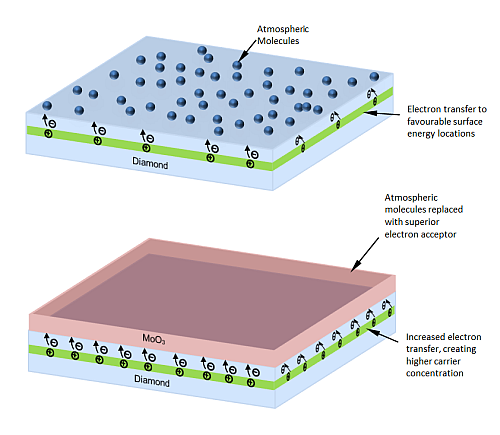
Recent work by the NEDDS group has demonstrated an improved process for higher efficiency and more stable doping of diamond.
September 2012
Diamond transistor with the highest cut-off frequency performance yet achieved made by the NEDDS group.
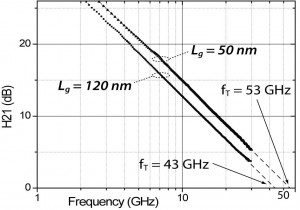
By optimising the processing used to make diamond transistors with a reduced gate length of 50 nm, devices with a cut-off frequency of 53 GHz have been demonstrated by the NEDDS group. This is the highest yet reported for a diamond based transistor.
This work was reported in the IEEE journal Electron Device Letters: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=6291745
Media Coverage:
http://www.semiconductor-today.com/news_items/2012/SEP/UNIGLASGOW_120912.html
May 2012
The NEDDS group make “the world’s smallest diamond coin” to commemorate Queen Elizabeth II’s Diamond Jubilee:

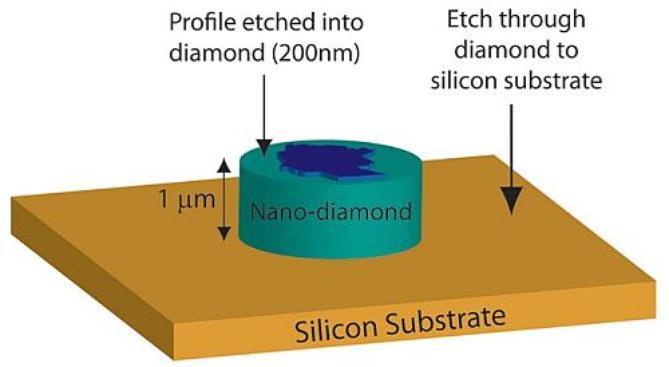
To help promote greater understanding and public awareness of the type of research undertaken by the NEDDS group and the nanofabrication capabilities of the James Watt Nanofabrication Centre, in 2012 Andrew Greer created a promotional diamond coin in commemoration of the Queen’s Diamond Jubilee.
The coin was created in two stages. First the profile of Queen Elizabeth was etched 200 nm deep into a film of nanocrystalline diamond on a silicon substrate.
Next, the circular shape of the coin was formed by etching through the remainder of the 1 um thick diamond layer to the silicon substrate. This deeper etch required to define the shape of the coin is less precise than the etch used to define the profile, which produces the roughness observed at the coin edges.
Some of the Jubilee Diamond Nano-Coin media coverage:
BBC news – http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-scotland-18273712
University of Glasgow – http://www.gla.ac.uk/news/headline_234253_en.html
The Times Newspaper – http://www.thetimes.co.uk/tto/news/uk/jubilee/article3432979.ece

